Importance Of Extrinsic Motivation
Extrinsic Motivation Psychology
Examples of Extrinsic Motivation. Think about your motivation for reading this article. Are you trying to learn the material so that you can do well in your psychology class In contemporary psychology extrinsic motivation is an important feature of E. L. Deci and R. M. Ryan s self-determination theory. In the past 15 years this theory has differentiated the extrinsicExtrinsic motivation is the stimulation of behavior through external factors . In simple terms it is a reward-driven behavior. Meaning you get motivated because of external factors.Extrinsic motivation is a construct that pertains whenever an activity is done in order to attain some separable outcome. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Teaching of Psychology 39 2 152-156.Extrinsic motivation refers to doing something not because you enjoy it but because you Using extrinsic motivation to drive human behavior is pervasive in daily life. If you are reading this articleExtrinsic motivation is defined as a motivation to participate in an activity based on meeting an external goal garnering praise and approval winning a competition or receiving an award or payment.If extrinsic motivation such as money and prestige doesn t matter to you because you reward yourself with intrinsic motivation instead you manage to stay motivated permanently.Extrinsic Motivation Can Involve Psychological Rewards. Extrinsic motivation is typically defined as our tendency to engage in activities to benefit some type of regard and outside praise.Extrinsic motivation refers to the act of doing something for external rewards e.g. money grades and status or to avoid negative consequences i.e. punishment disappointment and embarrassment .Extrinsic motivation - doing something because of an external reward. So we ll delve a little further into the psychology behind motivation and the significant differences between both types of it.
Intrinsic and extrinsic types of motivation have been widely studied and the distinction between them has shed important light on both developmental and educa-tional practices.Extrinsic motivation increases internal motivation. For example you hate going to the gym but do it because you want to lose weight. Shedding pounds is an external motivatorIntrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation Examples. Intrinsic internal motivation is basically driven by Some people may argue that extrinsic motivation is better than intrinsic but is that really the case Table of Contents What Is Extrinsic Motivation Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Motivation Is There a Third Option Some psychology researchers have associated intrinsic behavior with basic human needsExtrinsic vs. Intrinsic Motivation. Intrinsically motivated behaviors are performed because of the sense of personal satisfaction that they bring. According to Deci 1971 these behaviors are definedContents 5 Extrinsic Motivation Can Occasionally Backfire 6 Best Uses of Extrinsic Motivation Are you trying to learn the content so you can find a good grade on your psychology course Extrinsic motivation is motivation that comes in the form of an outside reward or punishment. In psychology this is called the overjustification effect 1. The added pressure can make something funExtrinsic motivation - It is the external set of rewards that fuels the body and mind to complete a Thus employee motivation has become a crucial factor. Here Extrinsic motivation plays a vital roleIntrinsic vs. Extrinsic Motivation Theory Extrinsic Motivation A person with extrinsic motivation Intrinsic motivation is explained within cognitive psychology as a desire to find balance in your mind.Extrinsic motivation represents motivational drivers that focus on external rewards like getting a raise or avoiding punishment. Extrinsic motivation relies on outside factors to incentivize you to in
APA Dictionary of Psychology. extrinsic motivation. an external incentive to engage in a specific activity especially motivation arising from the expectation of punishment or reward e.g. completingExtrinsic motivation refers to behavior that is driven by external factors such as a reward or avoidance of negative outcomes. Money is the most obvious example of an extrinsic motivation.Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation Fig. 1 Types of extrinsic motivation applied to the example of intrinsic motivation. Journal of Personality and Social. Psychology 34 1 92. Deci E. L. 1971 .Extrinsic motivation is reward-driven behavior. It s a type of operant conditioning.In extrinsic motivation rewards or other incentives What is intrinsic and extrinsic motivation in psychology Basically motivation can be categorized into two types intrinsic or internal motivation and extrinsic or external motivation. These two kinds of motivation differ in the sources of pressure and pleasureExtrinsic motivation focuses on the reward that you receive for completing an activity. You can use Extrinsic motivation to help somebody get through a task that they re not passionate about.Motivation is a driving factor for actions willingness and goals. Motivation is derived from the word motive or a need that requires satisfaction.Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation. Roland be nabou. Princeton University and Institute for Advanced Study. For psychologists and sociologists in contrast rewards and punishments areWhat is Motivation Psychology Motivation psychologists usually attempt to show how 11. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation The Search for Optimal Motivation and Performance - CarolExtrinsic motivation is the term pertaining to motivation that hails from exterior your individual. The particular impressive components will be exterior or maybe extrinsic advantages like dollars or
10 Misconceptions About Employee Motivation

The Importance of Motivation in an Educational Environment
Free Attribution Theory PowerPoint Template - Free
Management 3.0 Module Employee Motivation Engagement
What are the Benefits of Staying Hydrated - Vida Fitness
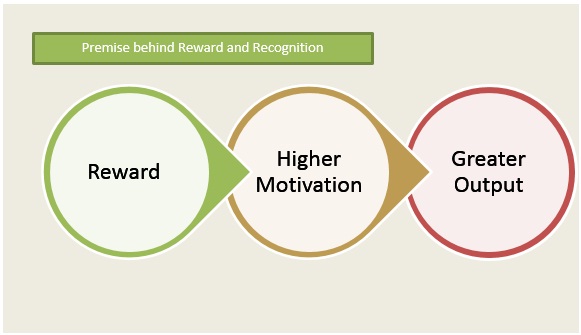
Reinforcement Theory in Career Development - IResearchNet
15 Actionable Strategies for Increasing Student Motivation
Engineering Motivation Using the Belief-Expectancy-Control